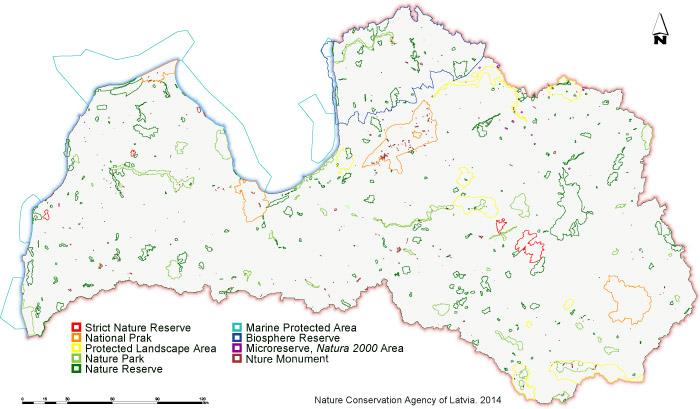
Specially protected nature territories in Latvia are geographical areas, that are under special state-level protection, in order to safeguard and maintain biodiversity of nature – rare and typical ecosystems, habitats for rare species,landscapes, that are peculiar, beautiful and characteristic for Latvia, geological and geomorphological formations, as well as territories, significant for recreational and educational purposes.
Updated: 05.12.2024.
In which categories are Latvian SPAs divided?
In accordance with the procedures specified in Latvian legislation, 658 SPAs have been established (excluding protected trees (big trees) and protected stones (big stones)), where each of them corresponds to one of the eight categories of protected areas - national park, biosphere reserve, nature park, protected landscape area, nature reserve, strict nature reserve, natural monument, marine protected area.
By 1 January 2020, 10543 large trees and 117 large stones have been identified and registered, as a result of which the total number of natural monuments has significantly increased (10990).
National parks are broad areas which are characterised by outstanding nature formations of national significance, landscapes and cultural heritage landscapes untouched by human activities or nearly natural, a diversity of biotopes, abundance of cultural and historical monuments, and peculiarities of cultural environment.
Biosphere reserve are broad territory in which landscapes and ecosystems of international significance are located. The goal of establishing biosphere reserves is to ensure the preservation of natural diversity and to promote sustainable social and economic development of the territory.
Nature parks are territories that represent the natural, cultural and historical values of a particular area, and that are suitable for recreation, education and the instruction of society. Organisation of recreation and economic activities in nature parks shall be carried out by ensuring the preservation of the natural, cultural and historical values located in such parks.
- Abavas senleja
- Adamovas ezers
- Aiviekstes paliene
- Bauska
- Beberbeķi
- Bernāti
- Cārmaņa ezers
- Cirīša ezers
- Daugavas ieleja
- Daugavas loki
- Doles sala
- Dridža ezers
- Driksnas sils
- Dvietes paliene
- Embūte
- Engures ezers
- Gaiziņkalns
- Istras pauguraine
- Kuja
- Kurjanovas ezers
- Laukezers
- Medumu ezeraine
- Milzukalns
- Numernes valnis
- Ogres ieleja
- Ogres Zilie kalni
- Pape
- Piejūra
- Pinku ezers
- Ragakāpa
- Riežupe
- Salacas ieleja
- Sauka
- Silene
- Svente
- Svētes paliene
- Talsu pauguraine
- Tērvete
- Užavas lejtece
- Vecumu meži
- Vilce
- Zvārdes meži
Protected landscape areas are territories remarkable for original and diverse landscapes and special beauty. The goals of such territories are to protect and preserve the cultural environment and landscapes characteristic of Latvia in all their diversity, as well as to ensure the preservation of environment appropriate for recreation of society and for tourism, and use of environment friendly management methods.
Nature reserves are nature territories little transformed or transformed in varying degrees by human activities, which territories include habitats of specially protected wild plant and animal species, and specially protected biotopes.
Strict nature reserves are territories untouched by human activities or nearly natural, in which territories unhindered development of natural processes shall be ensured in order to protect and study rare or typical ecosystems and parts thereof. Strict nature reserves shall have zones in which all natural resources are completely excluded from economic and other activities.
Marine protected areas are locations in the territorial sea, exclusive economic zone or continental shelf of the Republic of Latvia, which are established for the protection of protected biotopes and specially protected species habitat, as well as migratory bird significant feeding and wintering places.
Nature monuments are separate, isolated natural formations: protected trees, dendrological plantings, avenues, geological and geomorphological nature monuments and other natural rarities having scientific, cultural and historical, aesthetic or ecological value.
Microreserves are territories that are designated for the protection of specially rare species and their habitats. In microreserves similarly to specially protected natural territories certain actions that may threaten the rare species or their habitats are restricted or prohibited.
Microreserves are usually smaller than specially protected areas (0,1 – 20,0 ha, for birds up to 500 ha) and the establisment procedure is less complicated and shorter as than that of specially protected areas. Thus they ensure higher operativiness in the protection process.
The designation of microreserves is determined by the Law on the Protection of Species and Habitats, the Law on Forests and other subordinated regulations. The most significant of them are Cabinet Regulations No. 940 (18.12.2012.) Regulations Regarding Establishment, Protection and Management of Microreserves and Cabinet Regulations No. 421 (05.12.2000.) Regulations Regarding the List of Specially Protected Types of Biotopes.
As microreserves are established for the protection of especially rare species, the information regarding the microreserves and the species found in them is stored in the Data Base of Nature Conservation Agency and is available for registered users only.
Information on species and habitats in microreserves may be spread with a permission from the Nature Conservation Agency only.
What is Natura 2000?
All the countries of the European Union have made a co-decision to make a joint net of protected areas that is named Natura 2000. Since 2004 Latvia have joined this net. The existing specially protected areas were included in this net and it was replenished with 122 new territories. The main basis for including a new area in the net is protection of species of plants and animals and their habitats that are rare and endangered in Europe. The lists of these species and habitats are included in two directives of the European Union, and their protection is obligatory for all EU members. In the territory of Latvia 20 species of plants, 34 species of invertebrates, 29 species of mammals, 3 species of reptiles, 11 species of amphibians, 13 species of fish, 93 species of birds and 58 types of habitats.